IP Address VirtualMTAs
Adding an IP Address
This document describes how to use GreenArrow Engine’s web interface to add a new sending IP address. To update these settings by running SQL queries, see the Updating Throttle Settings in SQL page.
There are additional non-GreenArrow specific steps, described in the Adding a New IP Address FAQ page.
To create a new VirtualMTA that uses a new sending IP address, complete the following steps:
- Login to the GreenArrow Engine Web Interface.
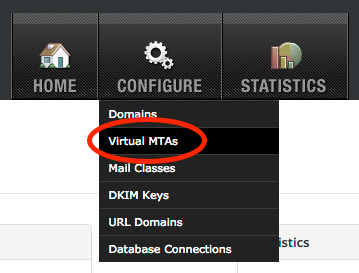
- Navigate to
Configure=>Virtual MTAs:
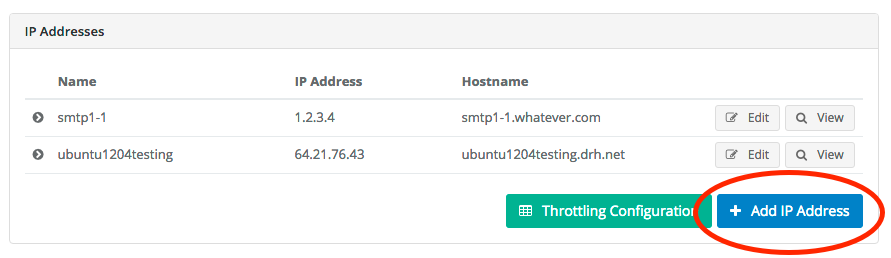
- Click the
Add IP Addressbutton:
- In the
Add IP Addressform, complete the following fields, then clickSave:-
Name- The name, or MTAid that you wish to assign this new VirtualMTA.- Must contain only ASCII characters in the range
0x20-0x7e; excluding comma, pound, and at-sign. - Must not have leading nor trailing whitespace.
- Must be unique (case-insensitive) across all types of VirtualMTAs (IP Addresses, Relay Servers, and Routing Rules).
- Must not also be an integer.
- Must be from 1 to 200 characters in length.
- Must contain only ASCII characters in the range
-
IP Address- the new IP address. -
Hostname- the reverse DNS record that was created for the new IP address. -
Redirect mail through another VirtualMTA- unchecked, unless you’d like to redirect mail through another VirtualMTA.
-
Throttling Template- select the desired throttling template. Each throttling template contains one or more throttling rules to apply to the IP address. -
Throttling Rules- you can add any desired throttle overrides to this section. These overrides will apply to just this IP address.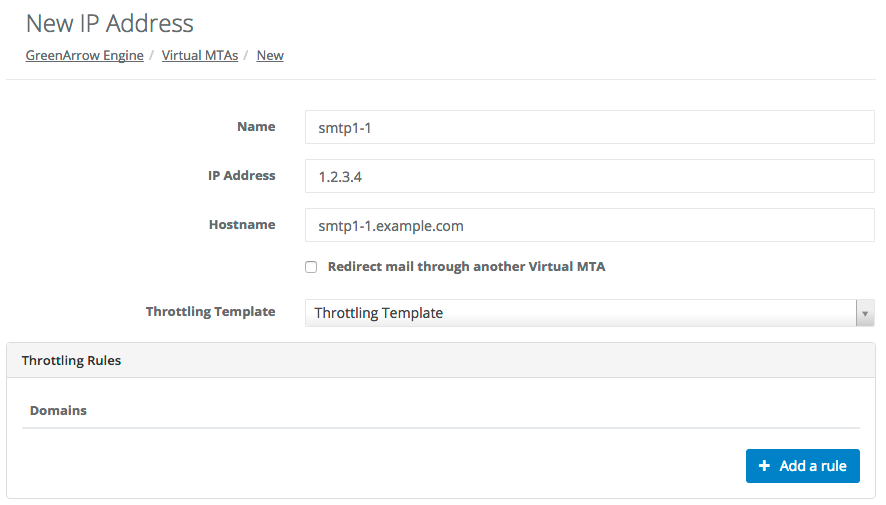
-
-
Send a test message using the new VirtualMTA. This is ideally done from the application that you normally use to send messages through GreenArrow so that the testing is end-to-end. If you’d like to perform a test on the command line, the following command can be run, replacing
smtp1-1with the name of the new VirtualMTA, and[email protected]with your email address:date | GREENARROW_MTAID=smtp1-1 /var/hvmail/bin/mailsubj "New VirtualMTA Test - smtp1-1" [email protected] -
Verify that you receive the test message, and examine the message’s headers to verify that the correct IP address and
HELOvalue were used to send the message. For example:Received: from smtp1-1.example.com (1.2.3.4)
Special Considerations when using NAT
If the new IP address uses NAT (Network Address Translation) to translate a private IP address to a public IP address, then there are some special considerations:
- When configuring DNS, use the public IP address, rather than the private IP address, since this is what recipient servers will see when your GreenArrow Engine server is sending messages.
- When filling in the
Add IP Addressform, theHostnameto enter is the reverse DNS record for the public IP address, rather than the private IP address, since this is what recipient servers will see when your GreenArrow Engine server is sending messages. - When filling in the
Add IP Addressform, the IP address to enter is the private IP address, since this is what was assigned to your Linux installation’s networking configuration. This private address probably starts with10.,172., or192.168.. - Add all public and private IP addresses (and localhost
127.0.0.1) to the/var/hvmail/control/replaceipmefile, one IP address per line. This file contains a list of IP addresses that this server should not deliver mail to on port25. If this file is missing, the default list contains all of the IP addresses locally assigned to the server. No step is required to apply changes to this file.
