Logging SMTP Sessions in GreenArrow
This document explains how to log SMTP sessions for incoming connections and outgoing connections. SMTP logging may be necessary while troubleshooting SMTP injection or delivery problems.
- Table of Contents
- Logging SMTP Sessions on Incoming Connections
- Logging SMTP Sessions on Outgoing Connections
- Caveats of SMTP logging
Logging SMTP Sessions on Incoming Connections
This can help identify issues during injection, or collect more information about injection problems.
The methods listed below apply to all SMTP services, but the example will be done on SMTP2, which is the service listening on port 587 (unless the default port for that service is changed).
Log SMTP Commands
SMTP command logging only logs the SMTP commands sent by the remote STMP client (the other party), and the responses sent by GreenArrow. It does not include the contents of the DATA request. This is usually enough to capture details about the session to identify problems while being less verbose than logging the full SMTP session.
To enable SMTP command logging, add the following line to /var/hvmail/control/smtp2 file and add the following line:
export GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_COMMANDS=
svc -tu /service/hvmail-qmail-smtpd2
Enabling SMTP Command Logging for a single IP
In some cases you want to enable SMTP command logging only for certain IP addresses.
To do this edit the IP authorization file, and add the GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_COMMANDS variable to the entry for the IP that you want to log SMTP commands for. And reload the authorization file configuration.
NOTE: the default authorization file is /var/hvmail/control/smtp.tcp unless you have configured additional authorization files - see the IPs Authorized to Relay documentation for details.
For example, assuming that you want to log the IP 1.2.3.4, and it is already authorized to inject messages with the follwoing line:
1.2.3.4:allow,RELAYCLIENT=""
Append the GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_COMMANDS="" variable to the authorization line. The result would be:
1.2.3.4:allow,RELAYCLIENT="",GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_COMMANDS=""
If the IP is not listed because the email client uses SMTP AUTH, then add an entry:
1.2.3.5:allow,GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_COMMANDS=""
Then apply the new configuration:
greenarrow config reload
Log SMTP Commands and Message
The procedure is the same when logging only SMTP commands:
(1) Edit the SMTP service file, for SMTP2 it is /var/hvmail/control/smtp2
(2) Append the following lines to log both commands and message:
export GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_COMMANDS=
export GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_MESSAGE=
svc -tu /service/hvmail-qmail-smtpd2
Log SMTP Commands and Messages for a single IP
Follow the same procedure for SMTP Command only logging:
(1) Edit the IP Authorization file (/var/hvmail/control/smtp.tcp by default)
(2) If there is an entry for the IP that you want to log, add the two variables. For example:
1.2.3.4:allow,RELAYCLIENT=""
Should become:
1.2.3.4:allow,RELAYCLIENT="",GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_COMMANDS="",GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_MESSAGE=""
(3) If the IP does not have an entry then add one:
1.2.3.5:allow,GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_COMMANDS="",GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_MESSAGE=""
(4) Apply the new configuration:
greenarrow config reload
Where is this information logged?
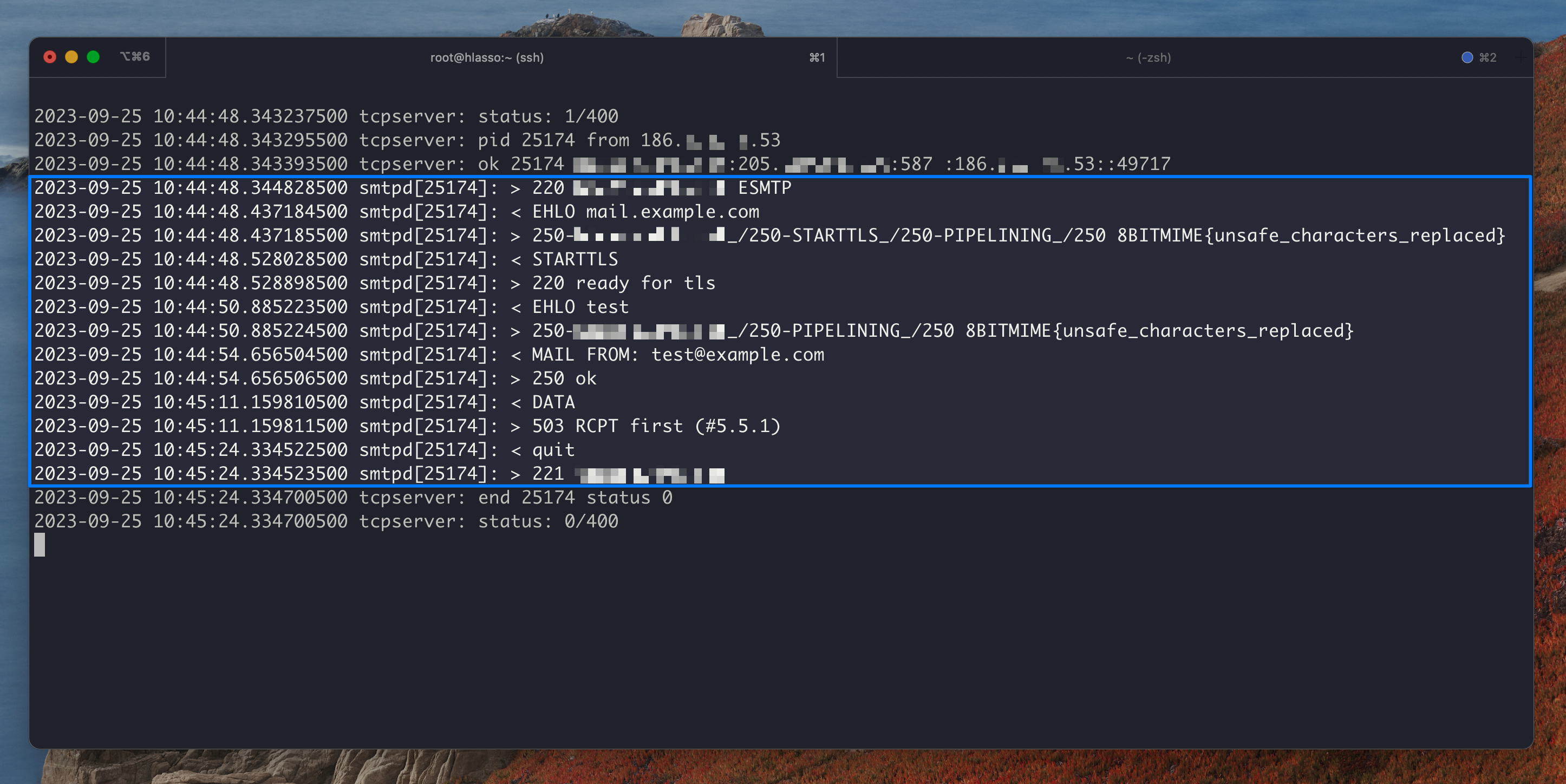
These SMTP sessions will be logged on the corresponding SMTP service log file.. You can monitor the SMTP2 log with the following command:
tail -F /var/hvmail/log/qmail-smtpd2/current | tai64nlocal
See this screenshot for an example:
Logging SMTP Sessions on Outgoing Connections
To log outgoing connections, use the directives log_smtp_connections, log_smtp_commands, or the log_smtp_hexdump directives.
These directives are added to GreenArrow’s main configuration file, and the logs are sent to the Rspawn Limiter service logs.
Log SMTP Commands
In this example, GreenArrow will log SMTP commands for outgoing connections, but only for connections to recipients at the domain example.com.
(1) Add the directive to the /var/hvmail/control/greenarrow.conf file
To log SMTP commands for messages sent to the domain example.com on all IP addresses add this block:
ip_address * {
domain example.com {
log_smtp_commands yes
}
}
(2) Validate and reload the new configuration (fix any syntax errors if needed and run again):
greenarrow config validate && greenarrow config reload
(3) Monitor the rspawn-limiter service log file:
tail -F /var/hvmail/log/rspawn-limiter/current | tai64nlocal
How to find SMTP logs
The rspawn-limiter file is a very verbose log, so using tools like tail may not be viable on busy systems.
Here are a couple of ideas to find SMTP command logs in the logs:
Filter output matching the pattern
“Tail” the log file using the command tail -F and use grep to filter lines that match the pattern. For example:
tail -F /var/hvmail/log/rspawn-limiter/current | tai64nlocal | grep " ([0-9]*) "
For more persistent logging, this command can be run in a tmux or screen session, and the output can be redirected to a temporary log file.
Find logs for a delivery attempt
The logdir_select_time command can be used to list entries in a log directory based on the provided time window. This can be combined with the hvmail_report tool to find SMTP logs for specific delivery attempts. Note that SMTP logging for outgoing messages must have been enabled at the time the delivery attempt took place.
For example, the following command prints the delivery attempts in the last 10 minutes to recipients at domain example.com:
hvmail_report -q all --last "10 minutes" --processed-logfile --human -r @example.com
And the output would look like this (edited for readability):
timestamp=<1726063521.17386> channel=<remote> status=<success> is_retry=<0> ...
msguid=<1726063520.92421863> recipient=<[email protected]> ...
sender=<return-t1-default240911-124-e49c16=2@DOMAIN> ...
The timestamp field is when the delivery attempt happened in UNIX EPOCH format. Use this timestampe to query the rspawn-limiter logs in a time window wrapping around the timestamp. For example, between 1726063500 and 1726063531.
Use the command logdir_select_time to query the log directory with this time window. In this example the output is sent to less to paginate the results:
logdir_select_time --start "1726063500" --end "1726063531" --dir /var/hvmail/log/rspawn-limiter | tai64nlocal | less
Or use pattern matching to print only SMTP log lines:
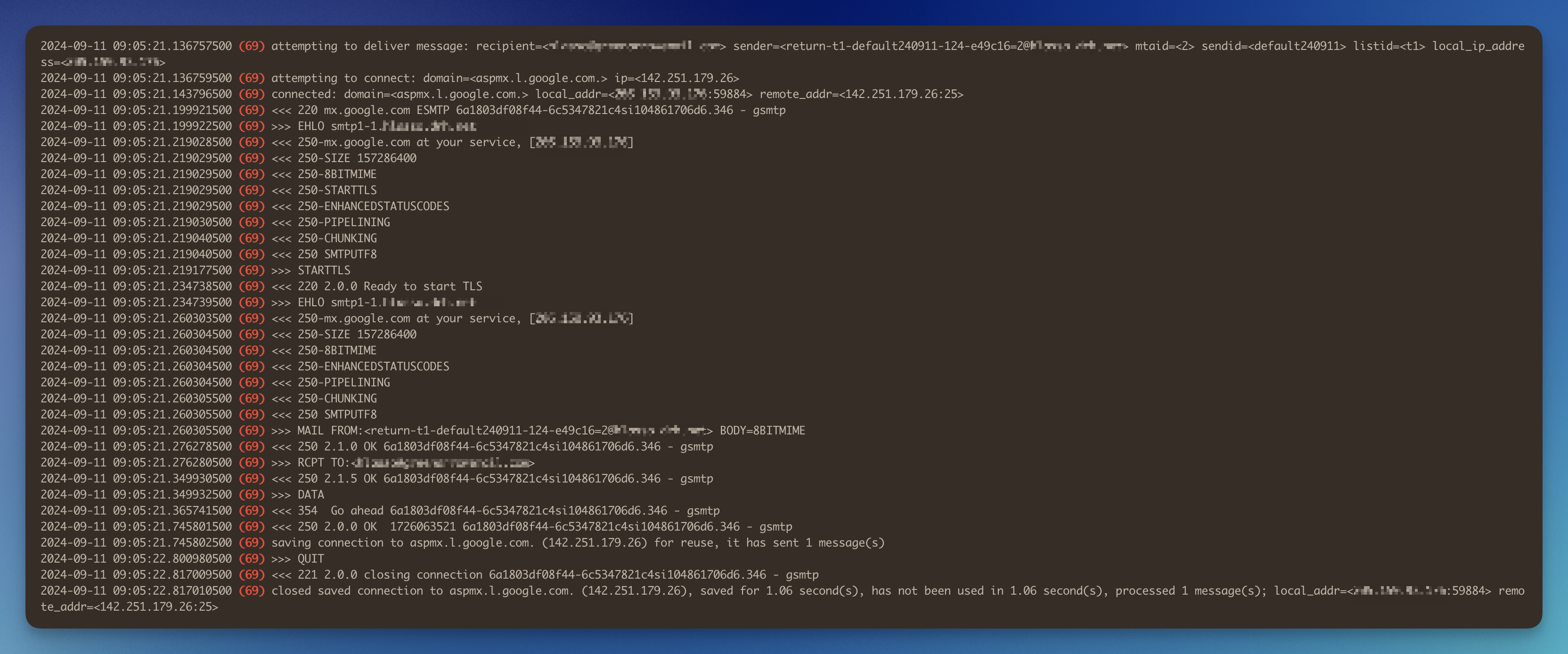
logdir_select_time --start "1726063500" --end "1726063531" --dir /var/hvmail/log/rspawn-limiter | tai64nlocal | grep " ([0-9]*) "
Here is an example of the output:
Caveats of SMTP logging
- SMTP logging is very verbose, log files will grow faster and will be rotated out more frequently. This is more noticeable when logging SMTP data
- Note that some SMTP logging options will include SMTP AUTH credentials. Take this into account when copying these logs to other systems, such as log aggregation applications
- SMTP data, logged with
GREENARROW_LOG_SMTP_MESSAGEorlog_smtp_hexdump, could contain other sensitive information if included in the message payload
To increase log file retention see the “Adjusting Log Retention” section in the Service Log documentation.
